Ultrasound’s Role In Detecting Medical Ailments
In the realm of modern medical diagnostics, ultrasound has emerged as a revolutionary tool that has transformed the way we detect and diagnose various medical conditions. With its non-invasive nature and high precision, ultrasound has become an indispensable tool in the hands of medical professionals.
From assessing pregnancies to evaluating musculoskeletal disorders, the applications of ultrasound are vast and diverse. In this article, we will delve into the world of ultrasound, exploring its different types, its role in detecting medical conditions, with a special focus on women’s ultrasound and musculoskeletal ultrasound. Additionally, we will discuss the concept of bulk-billed ultrasound and its advantages in healthcare accessibility.
What Is An Ultrasound?
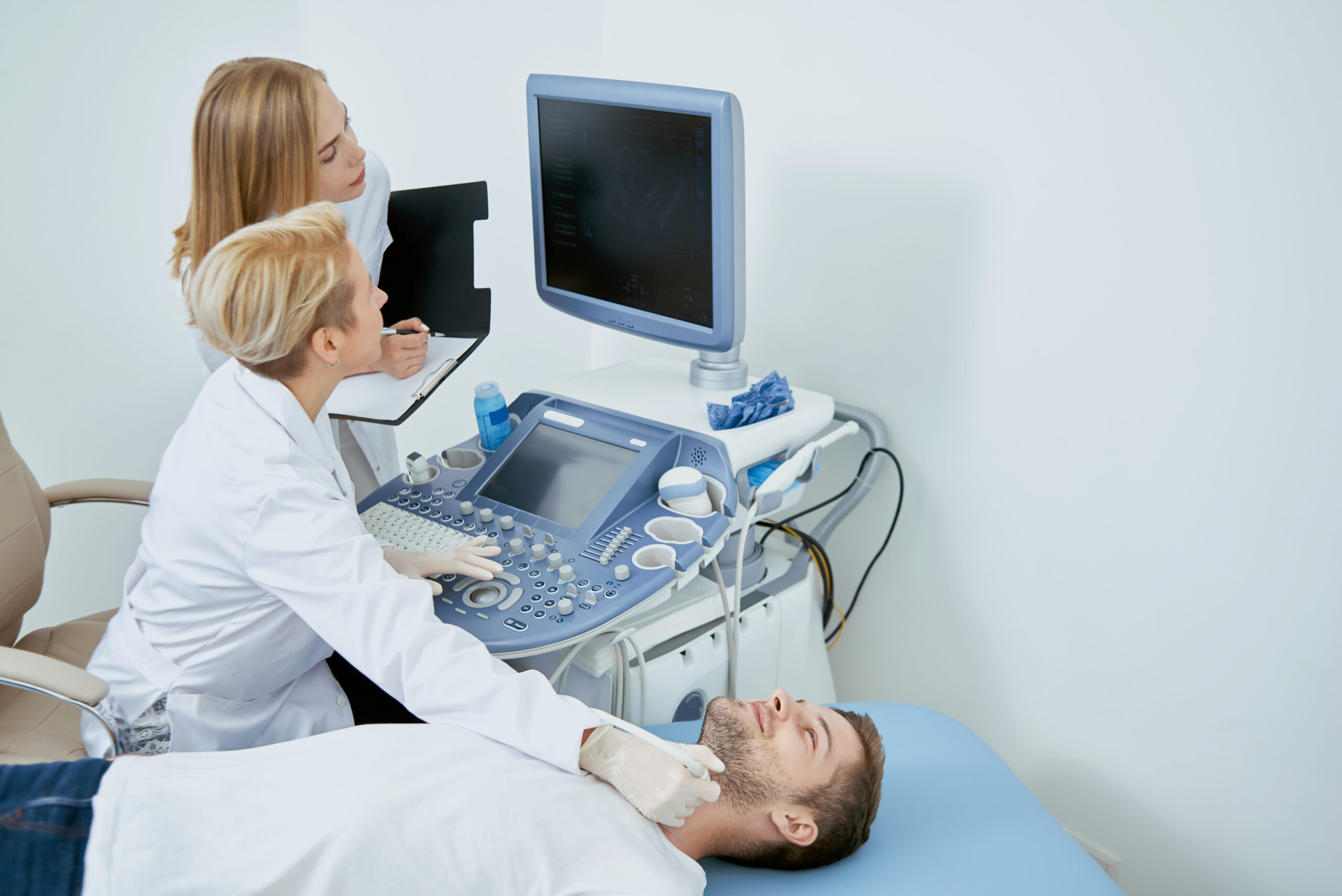
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the internal structures of the body. Unlike X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, ultrasound does not involve ionising radiation, making it safe for both patients and medical professionals.
The process involves the use of a transducer, which emits sound waves and captures the echoes as they bounce off different tissues. These echoes are then converted into visual images on a monitor, allowing healthcare providers to examine organs, tissues, and blood flow patterns.
Different Types Of Ultrasound
There are various types of ultrasounds designed to cater to specific medical needs. Here are the 12 major types of ultrasound.
Women’s Ultrasound: Women’s ultrasound plays a pivotal role in obstetrics and gynaecology. It is primarily used to monitor pregnancies, providing valuable information about the health and development of the foetus. This type of ultrasound helps in assessing the gestational age, detecting multiple pregnancies, evaluating foetal growth, and diagnosing any potential abnormalities. Furthermore, women’s ultrasound aids in the diagnosis of conditions like ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Musculoskeletal ultrasound is a powerful tool for evaluating disorders related to the bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. It enables physicians to visualise and assess conditions such as arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis, and muscle tears. One of the distinct advantages of musculoskeletal ultrasound is its ability to provide real-time dynamic imaging. This means that not only can the structure be examined, but also the movement and functionality of the affected area, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Abdominal Ultrasound: Abdominal ultrasound is utilised to examine the organs within the abdominal cavity. It helps diagnose conditions like liver disease, gallstones, kidney stones, pancreatic disorders, and abdominal masses. The non-invasive nature of this ultrasound makes it a preferred choice for initial diagnostic screening.
Cardiac Ultrasound (Echocardiography): Echocardiography is a specialised ultrasound used to assess the structure and function of the heart. It provides detailed images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns. Cardiac ultrasounds are crucial in diagnosing heart conditions such as heart valve defects, congenital heart abnormalities, and heart muscle disorders.
Vascular Ultrasound: Vascular ultrasound focuses on imaging the blood vessels and assessing blood flow. It aids in diagnosing conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT), arterial stenosis, aneurysms, and vascular insufficiencies. Doppler ultrasound, a subset of vascular ultrasound, adds the ability to assess blood flow velocity and direction.
Thyroid Ultrasound: Thyroid ultrasound is used to examine the thyroid gland and detect abnormalities such as thyroid nodules, goitres, and thyroid cancers. This type of ultrasound helps guide biopsy procedures and monitor changes in thyroid conditions.
Pelvic Ultrasound: Apart from women’s ultrasound, pelvic ultrasound is used in both genders to assess the pelvic organs. It aids in diagnosing conditions like prostate enlargement, testicular masses, and pelvic masses.
Transrectal And Transvaginal Ultrasound: These specialised ultrasounds are used to provide detailed imaging of the pelvic organs. Transrectal ultrasound is used for imaging the prostate gland in men, while transvaginal ultrasound offers detailed images of the female reproductive organs, especially the uterus and ovaries.
Neonatal Cranial Ultrasound: This type of ultrasound is performed on newborns to assess the brain’s structure and blood flow through the fontanelles (soft spots in the skull). It helps diagnose conditions like intraventricular haemorrhage in premature infants.
Ophthalmic Ultrasound: Ophthalmic ultrasound, also known as ocular ultrasound, is used to examine the eyes and the surrounding structures. It aids in diagnosing conditions like retinal detachment, tumours, and other eye-related abnormalities.
Prostate Ultrasound: Prostate ultrasound is used to assess the prostate gland in men, helping in the diagnosis and monitoring of conditions such as prostate cancer, prostatitis, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Paediatric Ultrasound: Paediatric ultrasound encompasses a wide range of applications to image various organs in infants and children. It assists in diagnosing congenital abnormalities, kidney issues, gastrointestinal disorders, and more.
Medical Conditions Detectable By Ultrasound
Ultrasound’s versatility extends to the detection and diagnosis of a wide array of medical conditions across various specialties. Some of the medical conditions that can be detected using ultrasound include:
Cardiovascular Conditions
Ultrasound, specifically echocardiography, is employed to evaluate the structure and function of the heart. It helps in diagnosing conditions such as heart valve abnormalities, congenital heart defects, and cardiomyopathies.
Furthermore, echocardiography plays a pivotal role in assessing the overall cardiovascular health of patients. It enables healthcare professionals to visualise the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns in real-time, providing essential information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. By detecting heart valve abnormalities, echocardiography assists in determining the severity of conditions like valve stenosis or regurgitation, guiding clinicians in making informed decisions about the most appropriate interventions, including surgical procedures or medication management.
Additionally, echocardiography’s ability to identify congenital heart defects is crucial for early intervention in infants and children, promoting better outcomes and improved quality of life. Its application in evaluating cardiomyopathies aids in understanding the structural and functional changes in the heart muscle, helping to tailor treatment strategies and monitor disease progression effectively. Overall, echocardiography’s non-invasive nature and detailed imaging capabilities make it an invaluable tool in diagnosing and managing a wide range of cardiovascular conditions.
Abdominal And Pelvic Conditions
Ultrasound is used to visualise the abdominal organs like the liver, kidneys, gallbladder, and pancreas. It aids in detecting conditions like gallstones, kidney stones, and liver tumours. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in examining the female reproductive organs, diagnosing conditions like ectopic pregnancies and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Moreover, ultrasound’s application in assessing abdominal and pelvic conditions goes beyond mere visualisation. By providing real-time images of the liver, kidneys, and other organs, ultrasound assists in the early identification of abnormalities such as cysts, tumours, and fatty liver disease. The ability to detect gallstones and kidney stones helps guide treatment decisions, whether through medical management or surgical intervention, promoting patient comfort and preventing complications. In cases of suspected liver tumours, ultrasound serves as an initial diagnostic step, aiding in determining the need for further testing or intervention.
When focusing on female reproductive health, ultrasound’s non-invasive nature makes it a valuable tool for assessing the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. This is particularly crucial in diagnosing conditions like ectopic pregnancies, where early detection can prevent life-threatening complications. Furthermore, ultrasound’s role in identifying pelvic inflammatory disease aids healthcare providers in promptly initiating appropriate treatment, reducing the risk of long-term reproductive health issues.
By providing detailed, real-time images of the abdominal and pelvic organs, ultrasound empowers healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and develop personalised treatment plans. Its versatility and safety profile make it an indispensable asset in managing a diverse array of medical conditions, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes.
Thyroid Disorders
Ultrasound assists in evaluating thyroid nodules, detecting their size, characteristics, and potential malignancy. This aids in determining the necessity for further testing or treatment.
Breast Abnormalities
Breast ultrasound is often used as a complementary imaging technique to mammography. It helps in distinguishing between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts, providing valuable information for breast cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
Musculoskeletal Disorders
As mentioned earlier, musculoskeletal ultrasound is pivotal in diagnosing conditions affecting bones, muscles, and joints. It aids in assessing joint inflammation, tendon tears, and other soft tissue abnormalities.
Advantages Of Bulk-billed Ultrasound
In many healthcare systems, the concept of bulk-billed ultrasound has gained significance due to its potential to improve healthcare accessibility and affordability. Bulk billing refers to a practice where healthcare providers bill the government or health insurance directly, ensuring that patients do not need to pay out-of-pocket expenses for the service. This has several advantages:
Affordability
Bulk-billed ultrasounds make medical imaging more affordable for patients, particularly those who might not have comprehensive health insurance coverage. This reduces financial barriers to accessing necessary healthcare services.
 Timely Diagnosis
Timely Diagnosis
The affordability factor encourages patients to seek medical attention and undergo necessary ultrasounds without delaying due to financial concerns. Timely diagnosis can lead to better treatment outcomes and improved patient well-being.
Preventive Care
Bulk-billed ultrasound promotes a culture of preventive healthcare by allowing patients to undergo regular screenings and diagnostic tests without financial constraints. This can aid in the early detection of medical conditions, facilitating early intervention and management.
Equitable Healthcare Access
Bulk billing promotes equitable access to healthcare services, bridging the gap between different socio-economic groups. It ensures that quality healthcare is accessible to everyone, regardless of their financial status.
Reduced Administrative Burden
For healthcare providers, bulk-billed ultrasounds streamline the billing process. Instead of managing individual patient payments and insurance claims, providers can focus more on patient care and medical procedures, ultimately leading to improved healthcare service quality.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
Affordable ultrasounds encourage patients to be more engaged in their own healthcare. When financial concerns are minimised, individuals are more likely to follow through with recommended medical tests and screenings, fostering a sense of responsibility for their well-being.
Early Intervention And Treatment
The availability of bulk-billed ultrasounds facilitates early intervention in medical conditions. Detecting issues at an early stage can lead to less invasive treatments, shorter recovery times, and reduced healthcare costs overall.
Support For Vulnerable Populations
Individuals from low-income backgrounds, elderly populations, and other vulnerable groups often face difficulties accessing necessary medical services. Bulk-billed ultrasounds can play a crucial role in addressing healthcare disparities and ensuring that everyone receives appropriate care, regardless of their socio-economic status.
Healthcare Cost Control
Bulk billing can contribute to overall healthcare cost control on a systemic level. By encouraging regular preventive care and early diagnosis, the healthcare system can potentially reduce the burden of treating advanced and more severe medical conditions, which tend to be more expensive.
Promotion Of Population Health
When a larger portion of the population can access affordable ultrasounds, the overall health of the community can improve. Detecting and managing health issues early on can lead to healthier individuals and a reduced strain on healthcare resources in the long run.
Strengthened Doctor-patient Relationships
The focus on patient care rather than financial transactions can foster stronger doctor-patient relationships. Doctors can concentrate on explaining medical conditions, treatment options, and addressing patient concerns, leading to more informed decision-making and increased patient trust.
Research Opportunities
With increased access to ultrasounds, healthcare systems have the potential to gather valuable medical data for research purposes. This data can contribute to medical advancements, treatment guidelines, and a deeper understanding of various health conditions.
Government And Policy Benefits
Bulk-billed ultrasounds align with government healthcare goals, as they promote preventive care and timely interventions. By supporting such practices, governments can work toward improving the overall health of the population and reducing the strain on public healthcare resources.
Innovation And Technological Advancements
As more patients have access to ultrasounds, the demand for improved imaging technology and techniques may rise. This can drive innovation in the field, leading to the development of more advanced and accurate diagnostic tools.
It’s important to note that while bulk-billed ultrasounds offer numerous advantages, there may also be challenges and considerations related to their implementation, funding, and impact on healthcare providers. A balanced approach that addresses both the benefits and potential limitations is essential for crafting effective healthcare policies and systems.
Conclusion
Ultrasound has undoubtedly revolutionised medical diagnostics, providing healthcare professionals with a safe, non-invasive, and effective tool to visualise and diagnose various medical conditions. From women’s ultrasound for monitoring pregnancies to musculoskeletal ultrasound for evaluating joint and soft tissue disorders, its applications are diverse and ever-expanding.
Moreover, the concept of bulk-billed ultrasound enhances healthcare accessibility, making these essential services more affordable and available to a broader population. As technology continues to advance, ultrasound’s role in detecting medical ailments will only become more prominent, contributing to improved patient care and outcomes.


 Timely Diagnosis
Timely Diagnosis
Leave a Reply